
Avoiding high churning and splash losses at low temperatures in gear boxes developing remedies for more efficient lubrication of bearings and lubricated joints and implementing a reliable and low- maintenance technology that enables vehicle wheel bearings to safely operate over wide temperatures require careful lubricant selection.įortunately, specially compounded mineral oils or synthetics are available that match cold flow requirements.1 In difficult cases, heating is needed for piping, reservoir and filters. Industries and transportation in northern parts of the United States, Europe and Canada are vulnerable to harsh outdoor conditions during winter months. As a result, machines often cannot start or excessive friction causes a complete failure. Dropping below the pour point and the higher viscosity not only restricts oil flow to bearings and other machine elements, but also translates into high startup torque. Just as an example, to calculate viscosity index we can use online viscosity index calculator or excel tools.Low ambient temperatures affect the flow characteristics of a lubricant.
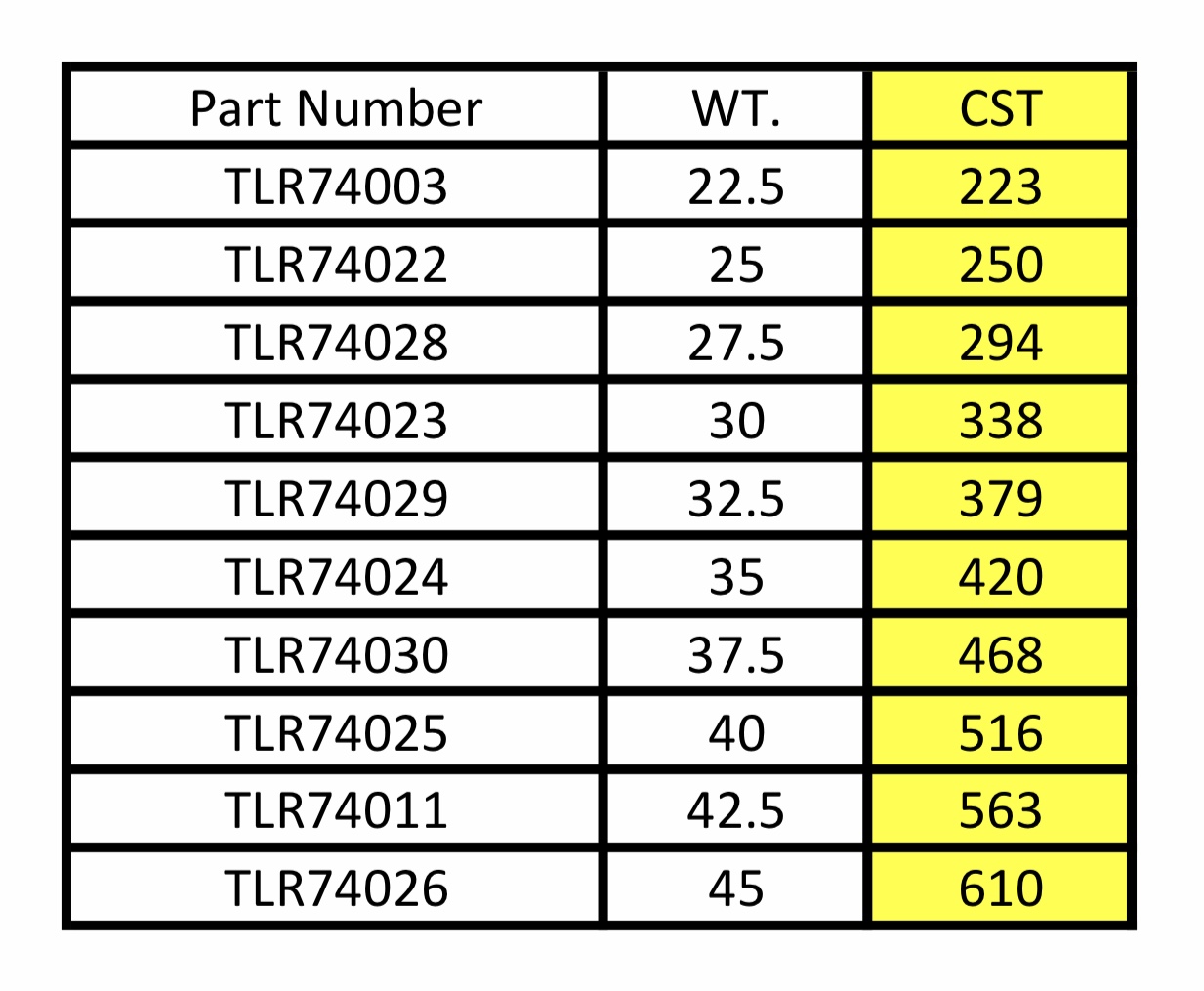
100 cst viscosity equivalents sae iso#
Common methods for viscosity index calculations are ASTM D2270 and ISO 2909.
100 cst viscosity equivalents sae how to#
Q: How to calculate viscosity index?Ī: The viscosity index of a fluid (usually oil) is calculated from its viscosity at 40 and 100☌. Therefore higher viscosity index or higher VI means fluid is more stable and less changes in viscosity over a wide temperature ranges. Viscosity index indicates the change in fluid viscosity in dependence of temperature. Q: What is viscosity index?Ī: Viscosity index of a fluid is a calculated number according to ASTM D2270 or ISO 2909. For example the viscosity of honey is higher than the water. High viscosity fluid has more resistance to flow than a low viscosity fluid. If viscosity of fluid is high, most likely it is difficult to pour. Hence high viscosity fluids flow less easily or slower. Low viscosity fluids (low resistance to move) flow or pour more easily and faster. Therefore oil/fluids are usually measured at the same temperature to calculate viscosity.


Lubricants Viscosity and Viscosity index Q: What is Viscosity?Ī: Viscosity is a fluid’s resistance to flow at given temperature. Press Calculate button to calculate kinematic viscosity (KV) As before, use Clear button to reset and calculate a new viscosity. Calculate Viscosity use calculator 3 to calculate viscosity (KV) Enter known viscosity index (VI) and kinematic viscosity (KV) in table 3. Click Calculate to get KV As previously stated, use Clear button to start a new calculation. Enter kinematic viscosity (KV) in the second row. Similarly with known viscosity index (VI) and viscosity It is possible to calculate viscosity For example enter viscosity index (VI) in the first row of second table. Calculate Viscosity possibility is to calculate kinematic viscosity from viscosity index. Finally, press Clear button to start again. Click Calculate button to get viscosity index (VI).
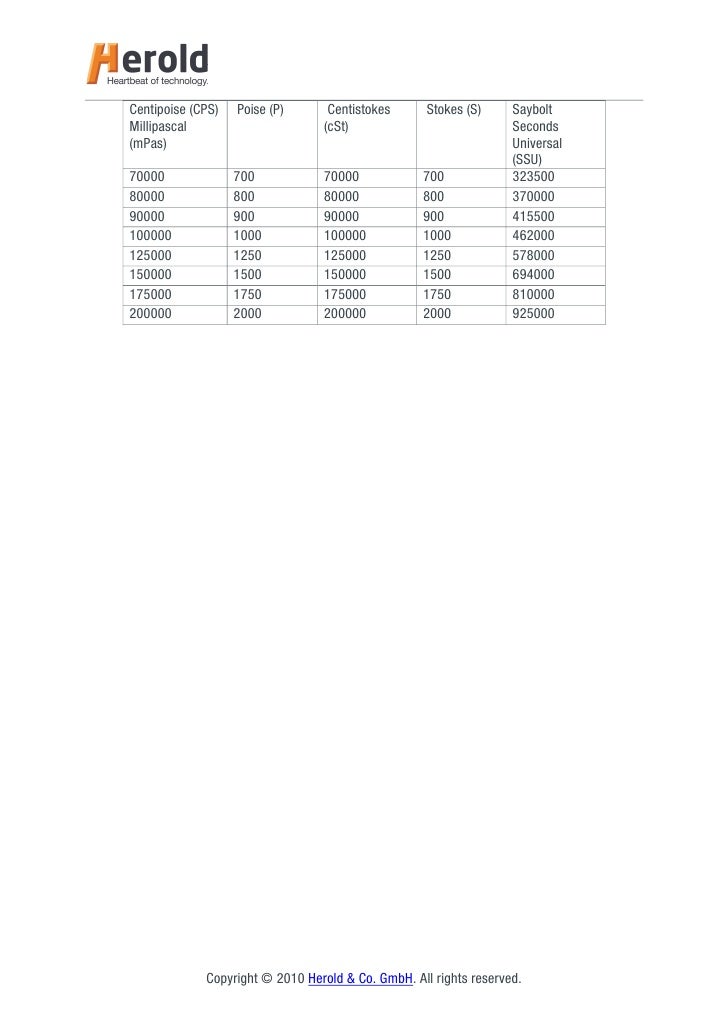
In the first row table 1, Enter kinematic viscosity (KV) at 40☌, In the same way enter kinematic viscosity in the second row. To calculate viscosity index we need viscosity of an oil both at 40☌ and 100☌. Standard practice for viscosity index (VI) calculation as per ASTM D2270 and ISO 2909.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
